Polymath POLY
Report IssueSentiment Neutral
Fundraising Statistics
$0 +3.68%
$0.4
 POLYPolymath
POLYPolymath
 USDCUSD Coin
USDCUSD Coin

Short Review Polymath
Crypto project Polymath (POLY) is classified as a Blockchain Service. Polymath is a Utility token that is hosted on the Ethereum Network. The current total supply is 1.00 B POLY (Circulating Supply + Tokens yet to be released - Burned Tokens).
Polymath ICO Overview
Estimated date for the public token sale: 12 January 2018. Polymath (POLY) price during the token sale: 0.4 USD. You can purchase project tokens for ETH
POLY Price Chart
The launch of POLY token trading took place on 11 August 2021.
Fundraising Rounds
Total sold 230.00 M POLY tokens (23.00% of total tokens). Total amount of funds raised by the Polymath project is $58.72 M.
| Investment Round | Date | Price | Funds Raised |
| Funding Round | January 2018 | $0.255 | $58.72 M |
Polymath Investors
Polymath (POLY) cryptocurrency
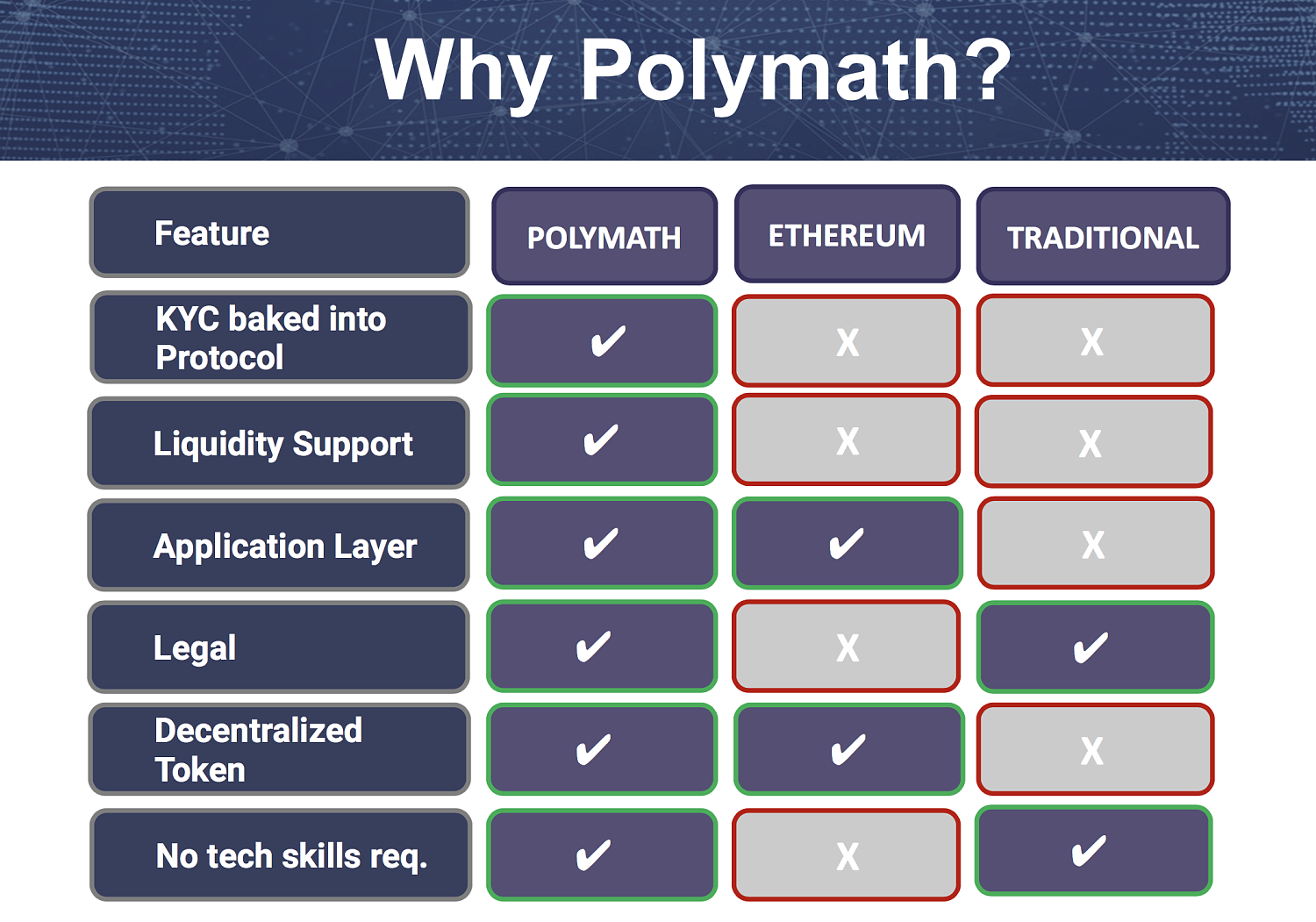
Polymath Network claims to be a revolutionary solution in the world of blockchains. The main goal of the project is tokenization of the securities market. Thus, Polymath develops and implements a decentralized platform. It combines the possibility of organizing an ICO and the regulation of a multi-billion dollar securities market, which can be built on blockchain technologies. The main focus is on interaction with legislation that facilitates or ensures the process of transferring securities into the digital space of the blockchain. This allows the project to avoid unnecessary complications and generate highly liquid assets. Polymath issues security tokens (ST) that comply with securities laws and regulatory authorities such as the SEC. The project team offers a full token issuance cycle, similar to how ICOs are conducted for regular utility tokens, but for Security Tokens, and this procedure is called STO (Security Token Offering). The result is ST-20 format tokens that are legalized and comply with regulatory requirements.
The ST-20 token type is an enhanced version of ERC-20, but the difference is that ST-20 has a number of capabilities not provided for for ERC-20. For example, ERC-20 tokens have no transfer restrictions and are therefore freely available for sale to anyone. If an organization plans to issue ST-20 tokens, it must ensure that the tokens can only be purchased by people who have completed the KYC or AML process and received approval. This allows security token issuers to comply with regulatory requirements due to transfer restrictions and other measures. The Polymath platform has its own ERC-20 utility token, POLY. It focuses on internal functionality and provides access to Polymath tools. The token also controls and ensures the functioning of internal transactions.
History of the Polymath (POLY) project
The Polymath project was created by Trevor Koverko and Chris Hausser in 2017. Trevor began his career working on Wall Street and then in Silicon Valley. Later, he became interested in the world of blockchain and began investing in projects such as Ethereum and EOS. The project team is based in Canada and consists of well-known professionals. Chris Hausser is interim CEO. Adam Dossa is currently the CTO and Mohammed Muraj is the General Counsel.
Polymath Advantages
- Liquidity. Asset tokenization allows issuers to combine multiple projects to attract institutional investors or split shares to enter the retail market. This is due to lower capital deployment and record keeping costs.
- High efficiency. Tokenization promotes high efficiency by removing outdated intermediaries and improving processes through reduced overhead, faster operation administrator and data transfer time.
- New asset classes. Another advantage of asset tokenization is that it not only improves the efficiency and liquidity of traditional assets (stocks, bonds and real estate), but also makes possible the emergence of new structured financial products.
Disadvantages of Polymath
- Incomplete decentralization. Most of the tokens are held by the project team , which indicates partial centralization.
- Negative influence from outside. Since the creation of security tokens is a fairly new solution, there is a possibility of negative influence or even suppression from established financial institutions.


 ByBit
ByBit  Gate
Gate  Score
Score